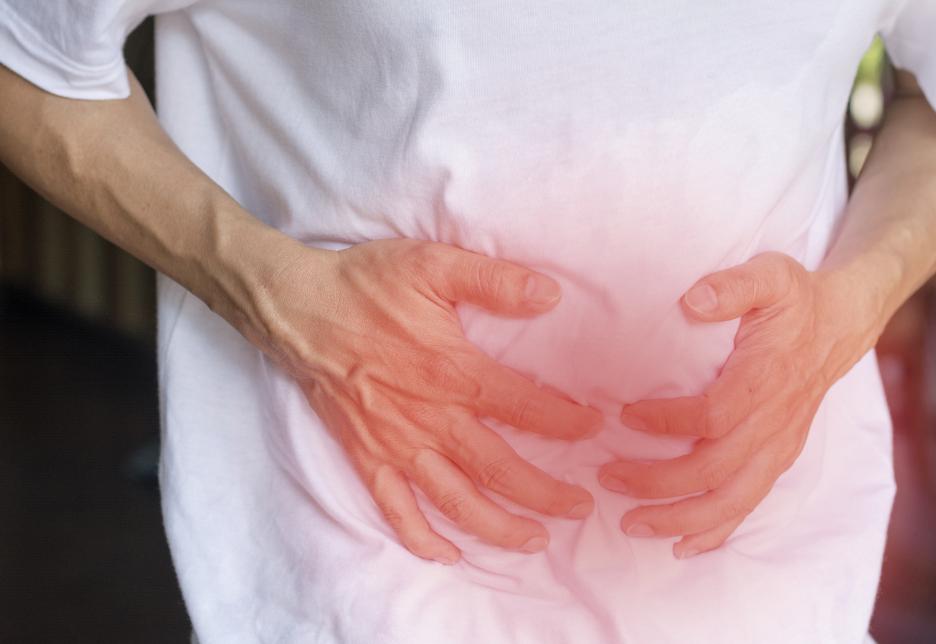
It is estimated that 1 in 5 adults in the United States have Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), a disorder that can cause abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. IBS is more common in women and usually begins around the age of 20. While there is no cure for IBS, there are treatments that can help manage the symptoms.
Dietary changes are often the first step in managing IBS. One common dietary change is to eat a high-fiber diet, which can help reduce constipation. Foods that are high in fiber include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and beans. It is also important to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids, especially water.
If dietary changes do not help, there are a number of medications that can be used to treat IBS. Anti-diarrheal medications, such as loperamide, can help to reduce diarrhea. However, these medications should not be used for more than two weeks. For constipation, laxatives may be recommended. These medications should only be used on a short-term basis, as they can cause dependence if used for too long.
In some cases, IBS may be caused by an underlying medical condition, such as celiac disease or inflammatory bowel disease. If IBS is thought to be caused by another condition, additional testing may be needed to confirm the diagnosis. Once a diagnosis is made, IBS can be managed with the help of a healthcare provider.
The original article can be found here: https://www.unifiedcaring.org/ten-tips-for-managing-irritable-bowel-syndrome-ibs-in-the-elderly-a-comprehensive-guide/?utm_source=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_campaign=ten-tips-for-managing-irritable-bowel-syndrome-ibs-in-the-elderly-a-comprehensive-guide